RAIN RFID Technology
RAIN RFID is a wireless technology that connects trillions of everyday items to the internet, enabling businesses and consumers to identify, locate, authenticate, and engage each item.
The RAIN Alliance is a global alliance promoting the universal adoption of UHF RFID technology in a way similar to other wireless technology organizations including NFC Forum, WiFi Alliance, and Bluetooth SIG. RAIN uses the GS1 UHF Gen2 protocol which ISO/IEC has standardized as 18000-63. The word RAIN—an acronym derived from RAdio frequency IdentificatioN—is intended as a nod to the link between UHF RFID and the cloud, where RFID-based data can be stored, managed, and shared via the Internet.
In simple terms, RAIN RFID is a passive, battery-free wireless technology that uses a reader to read and write a tagged item, manage the data, and take action. This enables businesses and consumers to identify, locate, authenticate, and engage with every item tagged with a RAIN RFID tag. RAIN RFID provides rich, real-time data and insights for a wide variety of applications including inventory management, asset tracking, and supply chain optimization across many industry sectors.
RAIN RFID is the fastest growing segment of the RFID market and has connected hundreds of billions of items to date providing the ability to:
- Uniquely identify individual items beyond just their product type
- Identify and locate items without direct line-of-sight
- Identify many items quickly (up to 1,000 items per second)
- Read items within a range of between a few centimeters to several meters
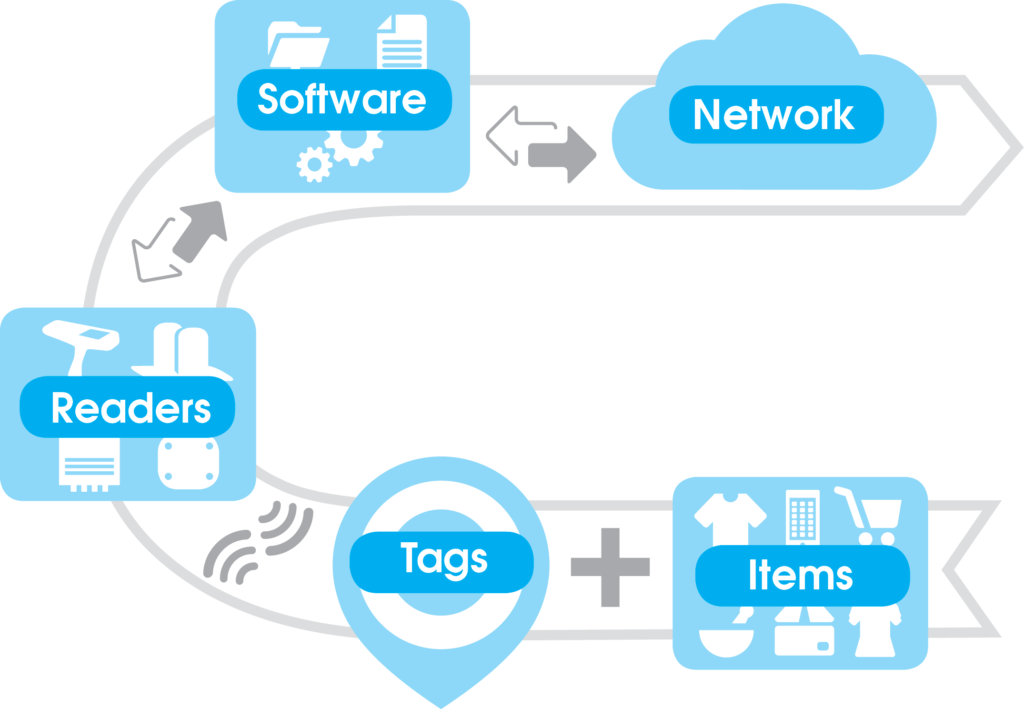
RAIN RFID Tags
- Are either attached to or embedded in items
- Tagged items store and send information
- Thousands can be identified simultaneously and do not have to be visible
RAIN RFID Readers
- Have antenna(s) for either short or long-range communication
- Can be small and portable, or larger and installed, or embedded in other devices
RAIN RFID Software applications
- Identify – Locate – Authenticate – Engage
- Use the tags and readers to create, collect, and use the item’s data – locally, on a server, or a cloud
- Authentication starts with determining whether an item is genuine
- Engage can involve sensors, or other means of interacting with the item
